
GLYCATION is a leading cause of Skin aging
- Most people have not heard about Glycation yet an average of 70% of the population have it. How your body processes sugar is determined in part by your genes.
- Glycation occurs when excess bodily glucose molecules link to the skin’s
- Collagen and Elastin fibers. This cross-linking can form chemical bridges
- between these proteins. Glycated collagen fibers can become rigid, less
- elastic and have reduced regenerative ability which can lead to damage
- such as laxity, cracking and thinning skin.
- Variations in the these genes can alter the functioning of normal glucose
- and energy metabolism. In addition, by consuming higher amounts of
- sugar intake with your lifestyle can override your genetic risk and can in
- turn create skin glycation issues
- INTERNAL SIGNS
- These signs generally occur
- BEFORE the age of 3
- VISIBLE SIGNS
- WEAK DERMAL EPIDERMAL JUNCTION
- Support structures within the skin begin to weaken
- loosing their ability to support the dermis. Overtime, areas
- begin to collapse inwards Eg, Wrinkles
- STIFFENED COLLAGEN FIBERS
- Leading to decreased elasticity. This is similar to rusty
- springs in a mattress, overtime it doesn’t quite bounce back
- as much
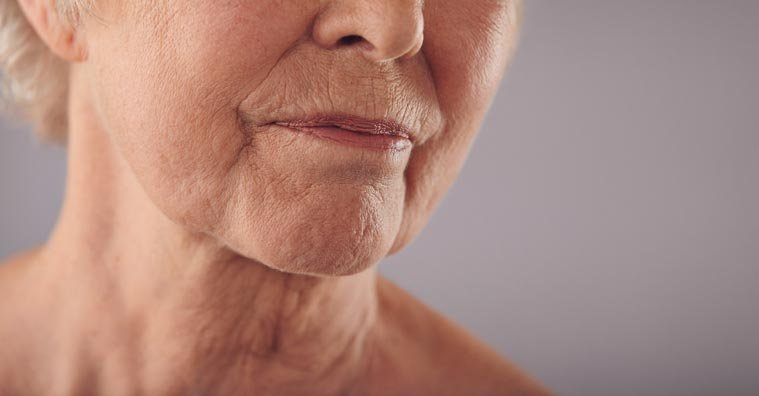
- HEAVY WRINKLES & FOLDS
- Upper lip and chin lines
- Vertical lines across cheeks
- Fine Lines
- AGING EYES
- Dryness and lines
- UNEVEN SKIN TEXTURE
- Rough surface area
- Leathery looking skin
- Crepey skin
A SkinDNA Genetic Test can determine your predisposition and to what degree you are susceptible to this aging process